Fake News has been an issue even before the internet era, but here in PH it was just generally known after being widely used on all political parties during the 2016 PH presidential election. I can’t stress enough the importance of media literacy thus I am delighted after learning about Lateral Reading and how to apply them to our daily information/news consumption.

Definition of Terms
Fake News – false stories that appear to be news, spread on the internet, or using other media, usually created to influence political views or as a joke. – Cambridge Dictionary
Lateral Reading – Instead of staying with one website or article, you might need to jump around a bit. Open multiple tabs in your browser to follow links found within the source and do supplemental searches on names, organizations, or topics you find. These additional perspectives will help you to evaluate the original article. – University of Texas
Lateral Readers – People who don’t spend time on the page or site until they’ve first gotten their bearings by looking at what other sites and resources say about the source at which they are looking.” – Web Literacy for Student Fact-Checkers – Mike Caulfield
Vertical Reading – Reading, staying, and finishing just one article or one website.
Headliner (news/article reader) – A person who only reads the headline of an article or news.
Truthiness – a quality characterizing a ‘truth’ that a person making an argument or assertion claims to know intuitively ‘from the gut’ or because it ‘feels right’ without regard to evidence, logic, intellectual examination, or facts.” Stephen Colbert
How to Apply Lateral Reading?
Always check the truth and accuracy of not just the article but its sources. You can follow or practice the ART of reading laterally. Check the Author, Reliability, and Target of the article.
Author – Who is the site/article author? What biases might the author have? Is the author authoritative source of the topic? What is the author’s motive behind the message? What can you learn about the author?
Reliability – How recent is the site or article? When was it published or updated? What other reliable sites say about the author and his/her claim?
Target – Who is the intended audience and why is the author targeting them? What does the author want from his/her target audience to believe, take a stand against, and/or support?
Every person has a certain truthiness in them and one reason why news sources factual evaluation has always been a heated argument. People have their favorite news sources and don’t like to be told that their news source is deceiving/untrustworthy.
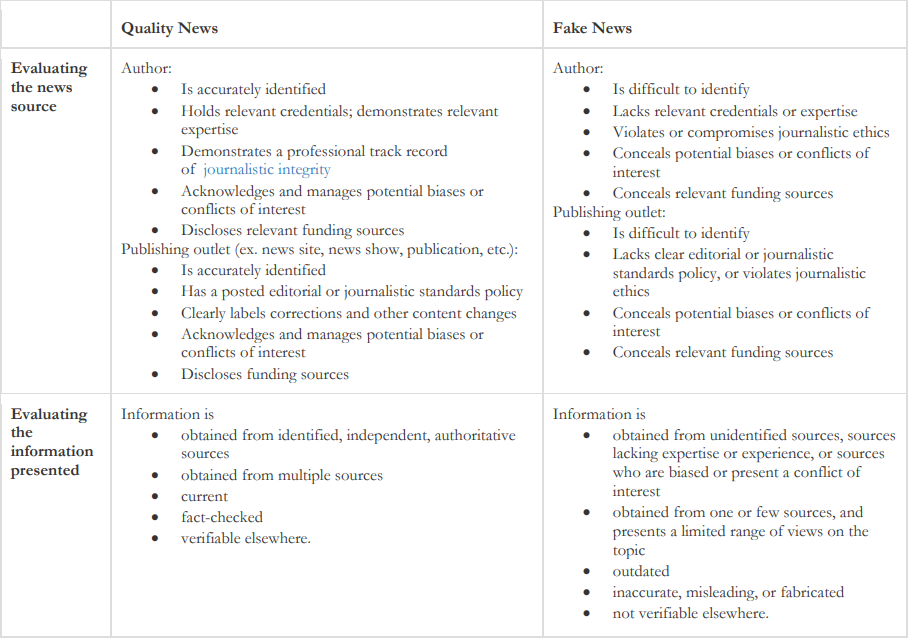
News Factual Checking
First, let us distinguish 2 important news activity:
Newsgathering – This is where news organization do investigative work (calling sources, research public documents, interview direct people involved, and checking and publishing facts)
News analysis – This is where the facts gathered are put together into a larger narrative.
What usually happens is that news media outlets do not list all facts on the news even though they do news gathering and news analysis. What has been added is the biases during the news analysis portion. To the extent that they only report news, they choose to cover, to whom they choose to target, and what they imply in the way they arrange those facts they have collected.
Those people who are only vertical readers will believe immediately what the news outlet has published limiting him/her the omitted facts during newsgathering. While lateral readers seek more and get all the facts about the news.
Narrative always and will always change a person’s perspective. If you are looking to validate a fact the questions are not just “What is the bias of this publication?” but also “What is this publication’s record with concern to accuracy?”
Other Things to consider and remember
• Not all top result in Google is factual and the best (some websites/organizations just have good SEO companies behind them) so take a moment to scan all search results and skim the snippets underneath the links.
• Not all professional looking website is credible. Follow the ART of Lateral Reading. You can first check the owner and contact person of the website through who.is, then look up the owner.
• You can use the Command-F keyboard shortcut to search within an article for a name, group, or word you can use on your fact-checking.
• Do not be afraid to leave the website. Right-click on links/anchor text to open a new tab.
We cannot eliminate fake news due to various biases and motives as humans, but we can help ourselves AVOID Fake News using Lateral Reading.
Stop being a headliner nor a vertical reader; practice the ART of LATERAL READING.
References
Lateral Reading and the Nature of Expertise
https://cor.stanford.edu/curriculum/collections/teaching-lateral-reading/
https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/c.php?g=539372&p=6876271
https://www.commonsense.org/education/lesson-plans/media-literacy-flex-your-fact-checking-muscles-read-laterally